Jacoco (opens new window) is the most common tool for retreiving test coverage. It supports different outputs like HTML, XML or CSV. I'd like to show you how to configure Jacoco in your Kotlin project with Gradle.
Let's start with a basic Gradle build file for a Kotlin project.
mkdir kotlin-gradle-jacoco
cd kotlin-gradle-jacoco
gradle init
mkdir -p src/main/kotlin/de/kevcodez
mkdir -p src/test/kotlin/de/kevcodez
buildscript {
ext.kotlin_version = "1.2.61"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version"
}
}
apply plugin: 'kotlin'
apply plugin: 'idea'
version = "0.1.0"
archivesBaseName = 'kotlin-gradle-jacoco'
group = 'de.kevcodez'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8:$kotlin_version"
}
compileKotlin {
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
}
compileTestKotlin {
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
}
Now that we've setup our basic project, we can start adding a new class.
package de.kevcodez
class SimpleService {
fun simpleMethod(boolean: Boolean?): Int {
return when {
boolean == null -> -1
boolean -> 1
else -> 0
}
}
fun uncoveredMethod() {
println("foo")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val simpleService = SimpleService()
println(simpleService.simpleMethod(true))
simpleService.uncoveredMethod()
}
Obviously, we want to test the service. JUnit 5 has been released a while ago and Gradle has native support for it. We have to make a few changes to the build script.
Add the following dependencies:
dependencies {
...
testImplementation "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.3.0-RC1"
testRuntimeOnly "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.3.0-RC1"
}
Next, we have to tell Gradle to use the JUnit platform. Edit the test task at the end of your build file.
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Great, now we can actually start writing our test.
package de.kevcodez
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
class SimpleServiceTest {
val simpleService = SimpleService()
@Test
fun `simple method test`() {
val result = simpleService.simpleMethod(true)
assertEquals(1, result)
}
}
We got everything set up. We have a working Kotlin Project with JUnit 5. But we don't have coverage reports yet. Gradle has an official plugin for Jacoco. For the last time, we have to edit the build script.
apply plugin: 'jacoco'
....
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
jacoco {
destinationFile = file("${buildDir}/jacoco/test.exec")
}
}
jacoco {
// You may modify the Jacoco version here
toolVersion = "0.8.2"
}
jacocoTestReport {
// Adjust the output of the test report
reports {
xml.enabled true
csv.enabled false
}
}
There are more options for configuring the coverage report. Take a look at the official plugin page (opens new window). After executing the test task (also included during build task, by default), execute the jacocoTestReport task. If it succeeds, reports are available under build/reports/jacoco/test. Our configuration generates a HTML report and a XML report.
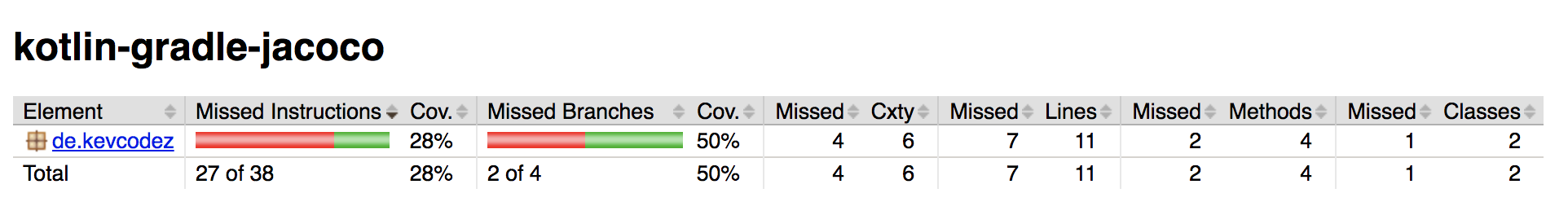
We're done. If you want to generate the report automatically, when executing the test task, you can add the following snippet to your build script:
test.finalizedBy(jacocoTestReport)
Check out the full source code on Github (opens new window).
If you like this post, feel free to follow me or hit me up on Twitter (opens new window).